Table of contents
- Understanding the Basics of Model Making
- Essential Tools and Materials
- Preparing Your Workspace
- Designing Your Model
- Choosing the Right Materials
- Cutting and Shaping Techniques
- Assembling the Model
- Detailing and Finishing
- Precision Measurement and Alignment
- Testing and Troubleshooting
- Documenting the Process
- Tips for Improving Precision
- Innovative Techniques and Technologies
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Engineering model making is not merely a craft; it is a critical component of the engineering design process. The success of a project can be substantially impacted by the precision of model creation, from concept validation to prototype testing. However, how do you attain that level of precision? Let us explore the strategies and methods that can assist you in the development of this complex skill.
Understanding the Basics of Model Making
Definition and Purpose
Model making in engineering involves creating physical representations of designs or concepts. These models help engineers visualize and test their ideas before full-scale production.
Historical Context
Model making has been around for centuries, with early examples found in ancient civilizations. Over time, it has evolved from simple wooden models to sophisticated prototypes using advanced materials and technologies.
Essential Tools and Materials
Cutting Tools
Precision starts with the right tools. Invest in high-quality cutting tools such as hobby knives, saws, and rotary tools. Each serves a different purpose, from rough cuts to intricate detailing.
Measuring Instruments
Accurate measurements are crucial. Tools like calipers, micrometers, and rulers ensure every piece fits perfectly, maintaining the model’s integrity.
Adhesives and Fasteners
Choose the right adhesives and fasteners based on your materials. Cyanoacrylate glue, epoxy, and mechanical fasteners like screws and bolts can offer strong, durable bonds.
Modeling Materials
Common materials include foam, plastic, wood, and metal. Each has its properties, advantages, and limitations, so select based on your project’s needs.
Preparing Your Workspace
Organizing Your Tools
A clutter-free workspace enhances efficiency and safety. Use tool organizers and storage solutions to keep your tools accessible and in good condition.
Ensuring Safety
Safety is paramount. Wear protective gear, ensure proper ventilation, and follow safety guidelines for using tools and materials.
Creating an Efficient Workflow
Plan your workflow to streamline the model-making process. Arrange tools and materials logically, and develop a step-by-step plan for your project.
Designing Your Model
Conceptual Sketching
Start with rough sketches to visualize your idea. These sketches serve as the foundation for more detailed plans.
Detailed Blueprints
Develop detailed blueprints with precise measurements and specifications. Blueprints guide the construction process and help identify potential issues early.
CAD Software
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software can enhance your design accuracy. It allows for precise measurements, adjustments, and virtual testing of your model.
Choosing the Right Materials
Material Properties
Understand the properties of different materials, such as strength, flexibility, and weight. This knowledge helps in selecting the best material for your model’s requirements.
Material Selection Criteria
Consider factors like cost, availability, and ease of handling when choosing materials. Balance these factors to optimize both performance and practicality.
Commonly Used Materials
Popular materials include polystyrene, acrylic, balsa wood, and aluminum. Each material has unique benefits, making them suitable for different aspects of model making.
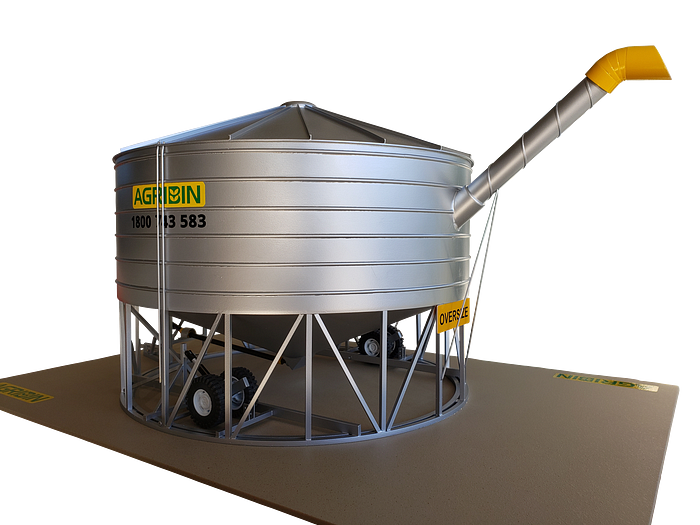

Cutting and Shaping Techniques
Basic Cutting Techniques
Master basic cutting techniques with tools like hobby knives and saws. Practice makes perfect, so start with simple cuts and progress to more complex shapes.
Advanced Shaping Methods
Advanced methods like laser cutting and CNC machining offer high precision. These techniques require specialized equipment but provide exceptional accuracy.
Tips for Accuracy
Measure twice, cut once. Double-check your measurements before making cuts to avoid costly mistakes.
Assembling the Model
Step-by-Step Assembly Process
Follow a systematic approach to assembly. Start with the main structure and gradually add smaller components, ensuring each piece fits correctly.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
Check the structural integrity at each step. Reinforce joints and connections as needed to maintain stability.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoid rushing the assembly process. Take your time to ensure each piece is aligned and securely attached.
Detailing and Finishing
Adding Fine Details
Details make your model stand out. Use fine tools and techniques to add intricate features that enhance realism.
Surface Finishing Techniques
Smooth surfaces and clean edges are crucial. Sanding, filing, and polishing can remove imperfections and prepare the model for finishing.
Painting and Texturing
Paint and texture add the final touch. Choose appropriate paints and techniques to achieve the desired look and feel.
Precision Measurement and Alignment
Using Calipers and Micrometers
Calipers and micrometers offer precise measurements. Use them to measure small components and ensure accurate dimensions.
Aligning Components
Alignment is critical for functionality and aesthetics. Use jigs and fixtures to hold components in place while assembling.
Ensuring Symmetry
Symmetry enhances visual appeal and performance. Double-check measurements and alignment to maintain balance.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Functional Testing
Test your model to ensure it works as intended. Functional testing can reveal design flaws or areas needing improvement.
Identifying and Fixing Flaws
Identify and fix flaws early. Small issues can escalate if not addressed promptly, affecting the overall quality.
Iterative Improvements
Model making is an iterative process. Use feedback from testing to refine and improve your model.
Documenting the Process
Keeping a Project Journal
Documenting your process helps track progress and learn from mistakes. Keep detailed notes, sketches, and photos throughout the project.
Photographing Your Model
Photograph your model at different stages. Photos provide a visual record and can be useful for presentations or portfolios.
Creating a Presentation
Summarize your project in a presentation. Highlight key steps, challenges, and solutions to showcase your skills and process.
Tips for Improving Precision
Practice and Patience
Precision comes with practice and patience. Spend time honing your skills and don’t rush through the steps.
Learning from Mistakes
Mistakes are learning opportunities. Analyze what went wrong and how you can avoid similar issues in the future.
Seeking Feedback
Seek feedback from peers or mentors. Constructive criticism can provide valuable insights and help you improve.
Innovative Techniques and Technologies
3D Printing
3D printing offers unprecedented precision and versatility. It’s ideal for creating complex shapes and detailed components.
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting provides high accuracy and clean edges. It’s perfect for intricate designs and repetitive tasks.
CNC Machining
CNC machining combines precision with automation. It’s excellent for creating detailed, consistent parts.
Conclusion
Mastering engineering model making requires a combination of skills, tools, and techniques. By focusing on precision, you can create models that are not only visually appealing but also functionally accurate. Remember, practice and patience are key. Keep refining your skills, learning from each project, and embracing new technologies. Your dedication to precision will pay off, resulting in high-quality models that stand out in the engineering world.
FAQs
How can I improve my model-making skills?
Practice regularly, learn from mistakes, seek feedback, and stay updated with new techniques and technologies.
What are the most common mistakes in model making?
Common mistakes include poor measurement, rushing the assembly process, and not double-checking alignment.
How do I choose the right materials for my model?
Consider the material properties, cost, availability, and ease of handling.
Shree Creators is a Mumbai-based engineering model makers firm that specializes in the production of highly detailed and precise architectural, industrial, and engineering models. Shree Creators is dedicated to excellence and innovation, providing customized solutions that adhere to the most stringent standards of precision and craftsmanship. We are dedicated to bringing your designs to life. Whether for presentations, prototypes, or educational purposes, our expert team ensures each model is a precise representation of your vision.
